
Retained earnings appear on the balance sheet under the shareholders’ equity section. Retained earnings can typically be found on a company’s balance sheet in the shareholders’ https://www.bookstime.com/ equity section. Retained earnings are calculated through taking the beginning-period retained earnings, adding to the net income (or loss), and subtracting dividend payouts.
- But while the first scenario is a cause for concern, a negative balance could also result from an aggressive dividend payout – e.g. dividend recapitalization in LBOs.
- The net income is obtained from the company’s income statement, which is prepared first before the statement of retained earnings.
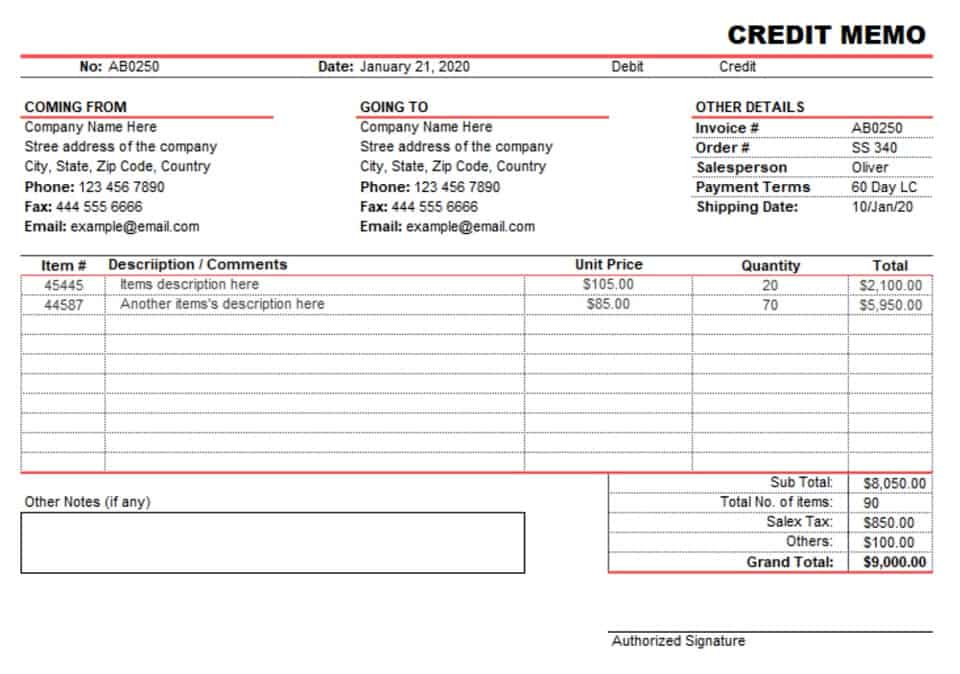
- In this case, Company A paid out dividends worth $10,000, so we’ll subtract this amount from the total of Beginning Period Retained Earnings and Net Profit.
- This is to say that the total market value of the company should not change.
- This statement is often used to prepare before the statement of stockholder’s equity because retained earnings is needed for the overall ending equity calculation.
- It also indicates that a company has more funds to reinvest back into the future growth of the business.
When financial statements are developed strictly for internal use, this statement is usually not included, on the grounds that it is not needed from an operational perspective. Yes, retained earnings carry over to the next year if they have not been used up by the company from paying down debt or investing back in the company. Beginning retained statement of retained earnings example earnings are then included on the balance sheet for the following year. Retained earnings are usually considered a type of equity as seen by their inclusion in the shareholder’s equity section of the balance sheet. Though retained earnings are not an asset, they can be used to purchase assets in order to help a company grow its business.
How to calculate retained earnings (formula + examples)
The beginning period retained earnings appear on the previous year’s balance sheet under the shareholder’s equity section. The beginning period retained earnings are thus the retained earnings of the previous year. Since stock dividends are dividends given in the form of shares in place of cash, these lead to an increased number of shares outstanding for the company. That is, each shareholder now holds an additional number of shares of the company. If the company is not profitable, net loss for the year is included in the subtractions along with any dividends to the owners. The dotted red box in the shareholders’ equity section on the balance sheet is where the retained earnings line item is recorded.
These include revenues, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and depreciation. As a result, additional paid-in capital is the amount of equity available to fund growth. And since expansion typically leads to higher profits and higher net income in the long-term, additional paid-in capital can have a positive impact on retained earnings, albeit an indirect impact. Revenue, sometimes referred to as gross sales, affects retained earnings since any increases in revenue through sales and investments boost profits or net income.
Open with the balance from the previous year
If a company has negative retained earnings, it has accumulated deficit, which means a company has more debt than earned profits. Generally speaking, a company with a negative retained earnings balance would signal weakness because it indicates that the company has experienced losses in one or more previous years. However, it is more difficult to interpret a company with high retained earnings. Over the same duration, its stock price rose by $84 ($112 – $28) per share. For an analyst, the absolute figure of retained earnings during a particular quarter or year may not provide any meaningful insight. Observing it over a period of time (for example, over five years) only indicates the trend of how much money a company is adding to retained earnings.
As mentioned earlier, retained earnings appear under the shareholder’s equity section on the liability side of the balance sheet. The disadvantage of retained earnings is that the retained earnings figure alone doesn’t provide any material information about the company. Retained earnings represent the portion of the net income of your company that remains after dividends have been paid to your shareholders. That is the amount of residual net income that is not distributed as dividends but is reinvested or ‘ploughed back’ into the company.
Additional Resources
If you have used debt financing, you have creditors or institutions that have loaned you money. A statement of retained earnings shows creditors that the firm has been prosperous enough to have money available to repay your debts. The statement of retained earnings is a sub-section of a broader statement of stockholder’s equity, which shows changes from year to year of all equity accounts. For example, during the period from September 2016 through September 2020, Apple Inc.’s (AAPL) stock price rose from around $28 to around $112 per share. During the same period, the total earnings per share (EPS) was $13.61, while the total dividend paid out by the company was $3.38 per share. Management and shareholders may want the company to retain the earnings for several different reasons.
S.S. Steel to acquire more fixed assets to boost capacity – Finance News: Latest Financial News, Finance News today in Bangladesh
S.S. Steel to acquire more fixed assets to boost capacity.
Posted: Mon, 27 Nov 2023 18:25:46 GMT [source]
Retained Earnings measure the accumulated profits kept by a company to date since inception, which were not issued as dividends to shareholders. The statement of retained earnings is also known as the retained earnings statement, the statement of shareholders’ equity, the statement of owners’ equity, and the equity statement. If the company has been operating for a handful of years, an accumulated deficit could signal a need for financial assistance.

